Clutch issues in bikes – we discuss the various problems faced by bikers related to clutch. In a lot of them you can save your costs…
Clutch is used to engage and disengage the engine from transmission while shifting the gears or while to run the engine at idle speed (gearless vehicles). A clutch is a flexible or releasable coupling which connects the adjacent ends of two coaxial shafts. Out of these two shafts, one shaft is crank shaft of an engine and another is an input shaft of a gear box.
It is said to be engaged or in, when the shafts are coupled and disengaged or out, when they are released. We in fact disengage the clutch when we press the clutch lever, otherwise it always remains in engaged position. All of us know that most of the bikes use wet multi plate type clutch to transmit the torque and power.
The use of multi plates is almost universal because there not as much of room is available in bikes to design the single plate clutch. So as a final point, designers uniformly share out the torque and power transmission between numbers of plate instead of single plate. Designers also foretell the life of clutch at the time of designing. Life of the clutch solely depends on frequency and handling of its exercise. Let us have brief outlook about the multi plate clutch assembly.
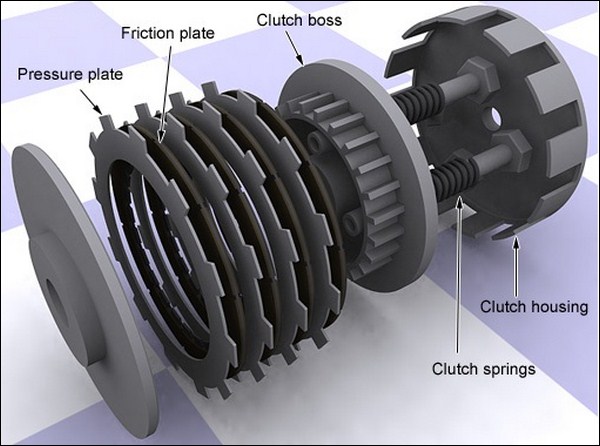
Parts of a Clutch Assembly
Multi plate clutch assembly consists following components:
- Clutch Housing
- Clutch Boss
- Clutch Springs
- Clutch Plates (Friction Plates)
- Pressure Plates
- Bearings
- Bushes
- Oil Seals
Out of above listed parts, commonly we have to replace the clutch plates and oil seals. Other components survive for very long time. Worker or service supervisor suggests us to replace the clutch plates and we blindly accept his proposal as genuine. Many of you must have also faced this at service stations. Likewise, many a times we could save a lot of our money. Therefore, let us discuss when do we really need to replace the clutch plates in our bikes.
Clutch Issues in Bikes
Clutch Slips While in Engagement
Clutch slip is the most objectionable fault that arises during rides. In clutch slip, friction between clutch plates and pressure plates diminish somehow. Slip causes loss of torque and power. You can feel it by twisting the throttle hard but not getting enough power at the rear wheel.
Possible Causes and Remedies: It is advisable to first check the adjustment of clutch wire with lever (engine casing). If the wire is over stretched, it results in poor engagement of clutch. It the wire is under stretched, it results in poor disengagement of the clutch. Both these practices are harmful to the friction surfaces of clutch plates.
So it is better to get recommended tension in clutch wire as soon as you feel the slip. This also adjusts the free clutch lever play (Free play is the initial small distance of lever up to which the clutch remains inoperative). If you let go this fault, it leads to worn out clutch facing after few weeks and you will have to replace the clutch plates as a result.
Another possible reason for clutch slip is weak or broken clutch springs. Clutch springs maintain the engagement of clutch plates and pressure plates. These springs drop their stiffness after long time. So if you are face this issue just replace the springs, not the clutch plates.
Clutch Drag or Burn
Contradictory to clutch slip, friction between clutch plates and pressure plates increases than the required. You can feel this as a difficulty in disengagement of the clutch. Disengagement becomes sticky because of melted friction surfaces. In excess cases, friction surfaces start burning because of overheating.
Possible Causes and Remedies: The very fundamental source of this fault is lack of lubrication. Friction between clutch plates and pressure plate increases because of less lubrication and so does the heat. High thermal stresses in plates increase the propagation of cracks on clutch plates and warping of pressure plates. It also tries to seize the clutch plates on the splined clutch shaft.
All these factors lead to the spongy feel and part disengagement of clutch. Because of incomplete disengagement, clutch plates and pressure plates always remain in contact generating more and more heat. This becomes a cyclic process and finally at critical temperatures, clutch starts burning.
But before a complete burn, the heated friction surface generates typical odour which can serve as a savior for your clutch. Clutch drag is possible even if your bike is sufficiently topped up with lubricating oil. This happens when rider shifts gears by partly engaging or without engaging the clutch. So the best possible remedy for clutch drag is to check the level of lubricating oil frequently.
How A Clutch Works? Its Parts and Types of Clutch
Clutch Judder
It is due to offensive engagement of the clutch. If the sudden forward jerk becomes a constant concern then it is clutch judder. You can feel the judder as an unsmooth engagement with vibrations that causes the vehicle to suddenly jump forward. It is not at all a resultant of worn out clutch plates. So don’t change the clutch plates on the spot if somebody suggests you as remedy of clutch judder.
Possible Causes and Remedies: Clutch judder is the result of misalignments or under tightened blots. Misalignment could be possible between plates, bearings and shafts, locks and pressure plates, spring seats and housing. Loose housing bolts, loose housing on flywheel, worn out shaft splines can also produce clutch judder. Sometimes engagement becomes jumpy because of distorted clutch plates also. In that case you don’t have any other option but to change the plates.
How Petrol Pump Attendants Cheat You – Quick Pointers
Clutch Rattle and Knock
Clutch rattle and knock are kinds of noises during engine idling and operating conditions respectively. You have to improve you observation skills to draw out the clutch rattle and knocking noise from the overall vehicle noise.
Possible Causes and Remedies: Both the undesirable noises are produced from worn out parts. These parts are worn bearings, worn clutch plates, worn out splines of shafts or plates. Here, worn out plates don’t mean the friction surfaces. Many times it happens that friction surfaces remain as it is but internal or external metal splines got worn out early.
Motorcycle Batteries: Explained in Detail
This causes little free movement of plates over the shafts and produces knocking noise at the time of engagement or disengagement. Same thing happens to the shaft bearings which produce rattling noise when engine runs idle. You can also replace these parts from secondary market if friction surfaces are still serviceable. That reduces the cost.
Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) in Motorcycles – Explained
Each of the above listed fault results in worn out friction surfaces and you have to change the clutch plates. But you can save your money by identifying the fault at an initial stage. Hope this article helped…
Next Read: “Which Engine Oil Shall I Use?” – Engine Oil Explained in Very Simple Terms
– Dhruv Panchal


