Long stroke vs short stroke engines – we discuss their characteristics along with examples in our motorcycle market…
Every time you read the technical specifications of motorcycles or generic auto related stuff on the internet, you may end up spotting some terms which you may not be aware of. In this story, we will discuss about the various types of engines that are available in motorcycles.
What is Engine Capacity?
The engine size or capacity is the amount of space the combustion chamber displaces and is measured in cubic capacity (volume, since it is a cylinder). For example, 220 cc, 150 cc engines mounted on various bikes.

Bore & Stroke
The engine capacity is measured as Bore x Stroke. Here, Bore is the diameter of the cylindrical block and Stroke is the depth of the cylindrical block, as shown in the following image.
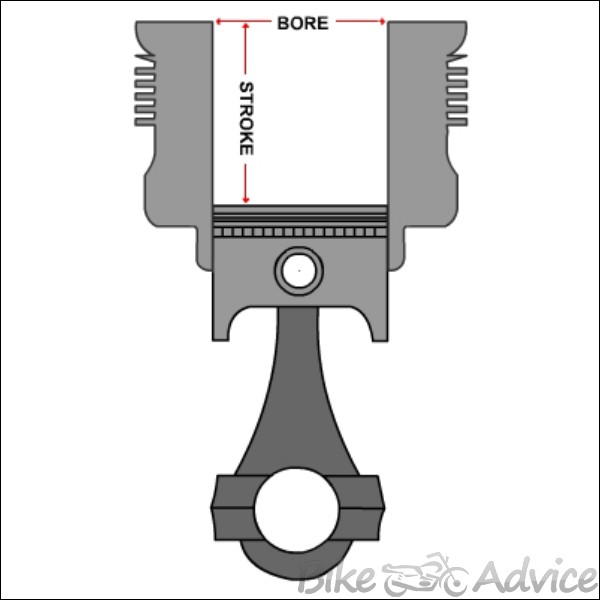
Types of Engines
It is this ratio of Bore and Stroke that categorizes the engine. There are three different types of configurations available depending on their ratio…
- Short Stroke Engines
- Long Stroke Engines
- Square Engines
Let us quickly discuss them along with examples…
Short Stroke/Over square Engine:
As the name signifies the Stroke is shorter than the Bore. Due to the relatively shorter stroke, the engine revs fast and is more suitable when quick build of power is required. Since the stroke does not have to travel far, it revs faster and can produce higher revs in lesser time.
A short stroke engine generally produces its peak power higher up the rev range. As a downside, the low speed tractability is relatively compromised.

Some examples:
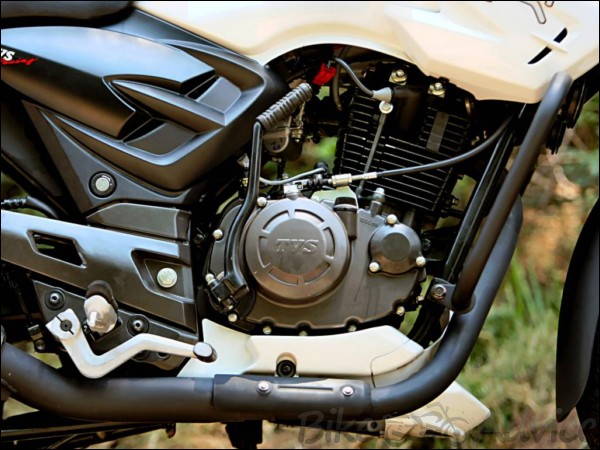
- Apache 180 – Bore = 62.5 mm and Stroke = 57.8 mm
- Pulsar 220 – Bore = 67 mm and stroke = 62.4 mm
- Speed 400 – Bore = 89 mm and stroke = 64 mm
Long Stroke/ Under square Engine:
As the name suggests the Stroke is longer than the Bore. Due to the longer stroke, the engine makes good torque at low rpms. It is important when the bikes’ pulling more (torque) at lower rpms is more important than the top speed.
Generally, tourers, cruisers and long distance motorcycles are preferred to have long stroke engines.
Informative: How Drum Brake Works? Explained with Pics

Some examples:
- Harley Davidson X440 – Bore = 79.6 mm and Stroke = 88.4 mm
- Royal Enfield Classic 350 – Bore = 72 mm and Stroke = 85.8 mm
- Hero Karizma – Bore = 65.5 mm and Stroke = 68.2 mm
- Honda CB350 – Bore = 70 mm and Stroke = 90.5 mm
Motorcycle Suspension, Working & Maintenance – Explained
Square Engine:
As a square has both the sides equal, here also the Bore and Stroke are of almost same size. This type of an engine tries to overcome the shortcomings of both the long stroke and short stroke ngines. In simple terms, it tries to strike a balance between torque and engine acceleration.
DiASiL Cylinder Vs Normal Cylinders – in Simple Terms
Some Examples:
- Yamaha FZ – Bore = 57.3 mm and stroke = 57.9 mm
- TVS Ronin – Bore = 66 mm and Stroke = 66 mm
Fuel Injection & Its Advantages – Quick Details

Tyre Ratings, Maintenance: All You Must Know About Tyres – in Simple Terms
Remember, these are inherent characteristics of these engines and can be over-ridden by various other ways. So, for example, the latest Speed 400 comes across as a short stroke engine but it has fairly good tractability (you can watch its review here).
– Kunal Chanana
Next Read: “Which Engine Oil Shall I Use?” – Engine Oil Explained in Very Simple Terms


