The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has been talking about a proposed Amendment to the Motor Vehicle Act for a long time now. After 2 years of scrutiny and recommendations, the Rajya Sabha has finally passed the historic 2016 Amendment. This will go a long way in the government’s aim to reduce accidents and fatalities by 50 per cent in the next 5 years.
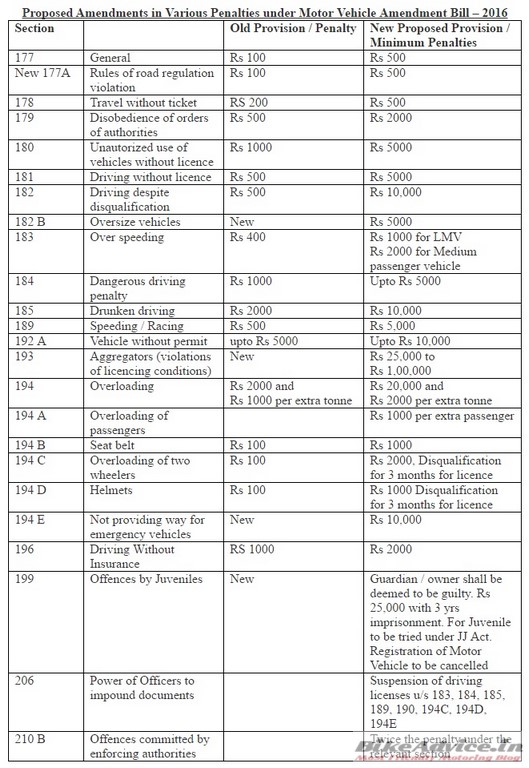
The new Amendment brings in changes on 68 of 223 sections with a severe increase in penalties for violation. Possibly the biggest reform in the Motor Vehicle Act ever also sees complete deletion of Chapter 10 while a new Chapter 11 has been introduced to simplify third party insurance claims and settlement processes.
The amendments mainly focus on issues relating to improving road safety and citizen’s facilitation while dealing with the Transport Department. Strengthening rural transport, last mile connectivity and public transport, automation and computerisation and enabling online services have also been kept in mind. The Bill also proposes to improve the transport scenario in the country by permitting the States to grant exemptions in Stage carriage and contract carriage permits for promoting rural transport, public transport, last mile connectivity and for passenger convenience and road safety.
Overspeeding fine has been raised from 400 bucks to Rs 1,000 while hit and run cases will have to pay a fine in the range of Rs 25,000 to Rs 2 lakhs. Fatalities will get up to Rs 10 lakhs while not wearing a helmet will cost you Rs 1,000. Carrying three people on a two wheeler? Get ready to pay Rs 2,000 or get your licence disqualified for 3 months. A new rule is that offences by juveniles will bring penalty on the guardians or owners. They face a fine of Rs 25,000 or 3 years of imprisonment.
In order to bring harmony of the registration and licensing process, it has been proposed to create separate national registers for driving licence vehicle registration through “Vahan” & “Sarathi” platforms. This will facilitate uniformity of the process across the country. The process for testing and certification for automobiles is proposed to be regulated more effectively. The testing agencies issuing automobile approvals have been brought under the ambit of the Act. Simultaneously, the driving training process has been strengthened enabling faster issuance of transport licenses. This will help in reducing the shortage of commercial drivers in the country.